The phrase "evidence-based" has become common knowledge.
But what exactly is "evidence"? Evidence is required in everything from scientific research to business decision-making.
This article is aimed primarily at those new to writing and explains the meaning of evidence and how to find it.
What is evidence?
Simply put, "evidence" means "proof" or "basis."
For example, if someone claims that "this medicine is effective against colds," then if there is data showing that many people took that medicine and their colds were cured, or the results of scientific experiments, this would be "evidence" for the claim that "this medicine is effective against colds."
In other words, when making a claim, evidence refers to objective facts that support the correctness of that claim.
Reference information:Evidence – Proposal to make "hospital jargon" easier to understand | National Institute for Japanese Language and Linguistics
Why evidence matters
The reason evidence is important is because it allows us to make decisions and take action based on objective, reliable information.
- Eliminate misinformation:
By choosing information that is based on scientific evidence rather than rumors or personal opinions, you can avoid being swayed by misinformation. - Better Decisions:
Evidence-based decisions are more likely to lead to better outcomes. For example, in the medical field, evidence-based treatment choices can improve patient outcomes. - The benefit to society as a whole:
Evidence-based policy-making contributes to the benefit of society as a whole. For example, evidence is used in a variety of situations, such as the approval of new medicines and the determination of education policy. - Scientific developments:
Evidence-based research is essential to scientific progress: new discoveries and theories are tested and developed based on previous research findings.
Evidence is not just information, but the basis for making decisions. By being aware of evidence, you will be able to make more objective and rational decisions, and live a better life.
Particularly important situations
- medical care: When evaluating the efficacy and safety of new treatments
- education: When verifying the effectiveness of teaching methods and curricula
- policy decision: When considering solutions to social problems
- Product Selection: When using this as a basis for product selection
merit
- health:
When choosing health information, choosing evidence-based information will help you manage your health more effectively. - economy:
When making product choices, having evidence-based information can help you avoid making unnecessary purchases. - Contribution to society:
By placing emphasis on evidence, we can prevent the spread of false information and contribute to more effective resolution of social problems.
Disadvantages
- information overload:
There is a huge amount of evidence, and it is difficult to examine it all. Too much information can make it even more difficult to make a decision. - Digital divide:
Much of the information requires specialized knowledge and can be difficult for the general public to understand. Information disparities can prevent people from making the right decisions. - Resistance to change:
New evidence is constantly emerging, so we need to adapt our lifestyles and mindsets to it. This can be overwhelming for people who fear change.
Types and levels of evidence
The types and levels of evidence are very important factors in evaluating the quality and reliability of research. Here, we will explain the types of evidence and the levels of their reliability in an easy-to-understand manner, even for beginners.
Types of evidence
There are two main types of evidence:
- Quantitative evidence: Evidence that can be expressed in numerical terms, such as experimental data, statistical data, etc.
- Qualitative evidence: Evidence that cannot be expressed in numerical terms. For example, interview results, observation records, etc.
Levels of Evidence
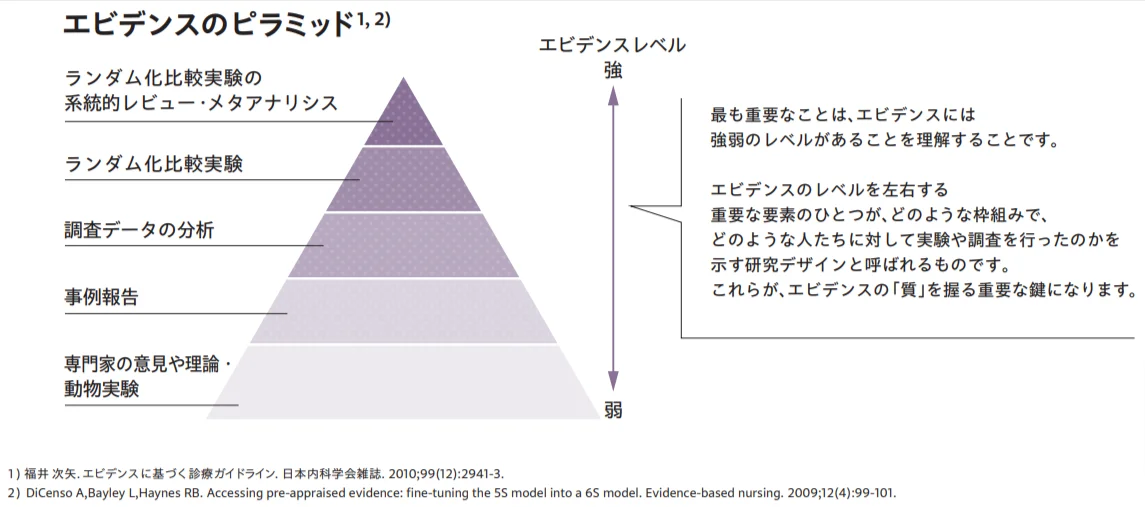
source:Textbook for health promotion measures | Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
There are levels of evidence. Generally, evidence obtained using more rigorous methods, such as randomized controlled trials, is considered to be more reliable.
The diagram above is the "evidence pyramid," which visually represents the level of reliability in the form of a pyramid.
The evidence pyramid is an index used to express the quality and reliability of research. There are many different types of research, each with a different level of reliability.
The higher you go up the pyramid, the higher the quality and reliability of the evidence.
Reference articles:
- Evidence-based health promotion | Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare
- Randomized Controlled Trial, Randomized (Comparative) Trial, RCT – Project to disseminate medical information in an easy-to-understand manner
How to find evidence
Many people want to search for "evidence" but don't know where to start.
We will explain how to search for evidence step by step, so even beginners can easily get started.
Clarify what you want to find out
First, be specific about what you want to find evidence about. For example:
"Effects of ○○ diet"
How to prevent ○○ disease
"Safety of ○○ product"
Your search will be more efficient if you ask specific questions, such as:
Choose a reliable source
When searching for evidence, it is important to choose reliable sources.
- Government Websites:
Data and reports released by government agencies such as the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology are relatively reliable sources of information. - Society website:
Guidelines and papers published by academic societies in each field can also be used as evidence. - University and research institute websites:
Research results published by universities and research institutes are also a valuable source of information. - Academic paper database:
You can search databases that contain specialized papers, such as PubMed and Google Scholar.
Set your keywords appropriately
Please search by substituting the keyword you want to find.
For example, if you want to search for "XX diet," you can narrow down your search by combining multiple keywords, such as "XX diet effects paper."
You can also use voice search on Google, so you can search using spoken language.
Evaluate the quality of information
You need to evaluate whether the information you find is truly trustworthy.
The following points will help you determine the reliability of information:
- author: Make sure that the authors of the paper or report are experts in their field.
- Year of publicationThe more up-to-date the information, the more reliable it tends to be.
- Research Methodology: Check that the survey is conducted using appropriate methods
- Sample size: Check if the number of survey subjects is sufficient
- Consistency with other studies: Check whether the results are consistent with other surveys or research findings
How to use evidence
There are various ways to use evidence effectively. Here, we will explain how to use evidence from three aspects: information gathering, decision-making, and communication.
Information gathering
- Identifying reliable sources of information:
Government reports, expert opinions, etc.Primary or secondary informationIdentify and collect reliable sources of information. - Keyword Search:
You can search for information more efficiently by using keywords that are specific to the subject you want to search for. For example, "health benefits of ____" or "measures for ____." - Collecting information from multiple sources:
By collecting information from multiple sources rather than just one, and comparing and examining it, you can make a more objective decision. - Beware of biases and cognitive distortions:
Confirmation bias, halo effect,Zero hundred thinkingThis can distort the way information is received and the judgments made.
decision making
- Understanding the current situation:
We conduct evidence-based data analysis to accurately understand the current situation.Correlation vs. CausationAlso, be careful. - Evaluating the options:
The pros and cons of each option are assessed based on the evidence. - Assessing risk:
The risks associated with each option are assessed based on the evidence. - decision making:
Based on the results of the above evaluation, choose the most suitable option.
communication
- Persuasive presentations:
Using evidence-based data and graphs will help you make a more persuasive presentation. - Facilitating the exchange of ideas:
Sharing evidence can promote the exchange of opinions from an objective perspective. - consensus building:
Through evidence-based discussion, it becomes easier to gain consensus from more people.
Points to note when using
- Quality of information:
Please check the reliability of the information, the time of publication, etc. You should avoid making decisions based on outdated or unreliable information. - Information bias:
Be careful not to be biased towards information that represents a particular position or interest. - Terminology:
If you don't understand a technical term, you will need to look it up in a dictionary or on the Internet.
summary
Evidence is not just information, it is evidence. To find effective evidence, it is important to identify reliable sources and to have a critical eye.
I believe that by acquiring evidence-based thinking, you will be able to make more objective and rational decisions.


